Jeff Parker – Suite ...

 Album Info
Album Info
“I’m always looking for ways to be surprised,” says composer and multi-instrumentalist Jeff Parker as he explains the process, and the thinking, behind his new album, Suite for Max Brown, released via a new partnership between the Chicago–based label International Anthem and Nonesuch Records. “If I sit down at the piano or with my guitar, with staff paper and a pencil, I’m eventually going to fall into writing patterns, into things I already know. So, when I make music, that’s what I’m trying to get away from—the things that I know.”
Parker himself is known to many fans as the longtime guitarist for the Chicago–based quintet Tortoise, one of the most critically revered, sonically adventurous groups to emerge from the American indie scene of the early nineties. The band’s often hypnotic, largely instrumental sound eludes easy definition, drawing freely from rock, jazz, electronic, and avant-garde music, and it has garnered a large following over the course of nearly thirty years. Aside from recording and touring with Tortoise, Parker has worked as a side man with many jazz greats, including Nonesuch labelmate Joshua Redman on his 2005 Momentum album; as a studio collaborator with other composer-musicians, including Makaya McCraven, Brian Blade, Meshell N’Degeocello, his longtime friend (and Chicago Underground ensemble co-founder) Rob Mazurek; and as a solo artist. Suite for Max Brown is informally a companion piece to The New Breed, Parker’s 2016 album on International Anthem, which London’s Observer honored as the best jazz album of the year, declaring that “no other musician in the modern era has moved so seamlessly between rock and jazz like Jeff Parker. As guitarist for Chicago post-rock icons Tortoise, he’s taken the group in new and challenging directions that have kept them at the forefront of pop creativity for the last twenty years. As of late, however, Parker has established himself as one of the most formidable solo talents in modern jazz.”
Though Parker collaborates with a coterie of musicians under the group name The New Breed, theirs is by no means a conventional “band” relationship. Parker is very much a solo artist on Suite for Max Brown. He constructs a digital bed of beats and samples; lays down tracks of his own on guitar, keyboards, bass, percussion, and occasionally voice; then invites his musician friends to play and improvise over his melodies. But unlike a traditional jazz session, Parker doesn’t assemble a full combo in the studio for a day or two of live takes. His accompanists are often working alone with Parker, reacting to what Parker has provided them, and then Parker uses those individual parts to layer and assemble into his final tracks. The process may be relatively solitary and cerebral, but the results feel like in-the-moment jams—warm-hearted, human, alive. Suite for Max Brown brims with personality, boasting the rhythmic flow of hip hop and the soulful swing of jazz.
“In my own music I’ve always sought to deal with the intersection of improvisation and the digital era of making music, trying to merge these disparate elements into something cohesive,” Parker explains. “I became obsessed maybe ten or fifteen years ago with making music from samples. At first it was more an exercise in learning how to sample and edit audio. I was a big hip-hop fan all my life, but I never delved into the technical aspects of making that music. To keep myself busy, I started to sample music from my own library of recordings, to chop them up, make loops and beats. I would do it in my spare time. I could do it when I was on tour—in the van or on an airplane, at a soundcheck, whenever I had spare time I was working on this stuff. After a while, as you can imagine, I had hours and hours of samples I had made and I hadn’t really done anything with them
“So I made The New Breed based off these old sample-based compositions and mixed them with improvising,” he continues. “There was a lot of editing, a lot of post-production work that went into that. That’s in a nutshell how I make a lot of my music; it’s a combination of sampling, editing, retriggering audio, and recording it, moving it around and trying to make it into something cohesive—and make it music that someone would enjoy listening to. With Max Brown, it’s evolved. I played a lot of the music myself. It’s me playing as many of the instruments as I could. I engineered most it myself at home or during a residency I did at the Headlands Center for the Arts [in Sausalito, California] about a year ago.”
His New Breed band-mates and fellow travelers on Max Brown include pianist-saxophonist Josh Johnson; bassist Paul Bryan, who co-produced and mixed the album with Parker; piccolo trumpet player Rob Mazurek, his frequent duo partner; trumpeter Nate Walcott, a veteran of Conor Oberst’s Bright Eyes; drummers Jamire Williams, Makaya McCraven, and Jay Bellerose, Parker’s Berklee School of Music classmate; cellist Katinka Klejin of the Chicago Symphony Orchestra; and even his seventeen-year-old daughter Ruby Parker, a student at the Chicago High School of the Arts, who contributes vocals to opening track, “Build A Nest.”
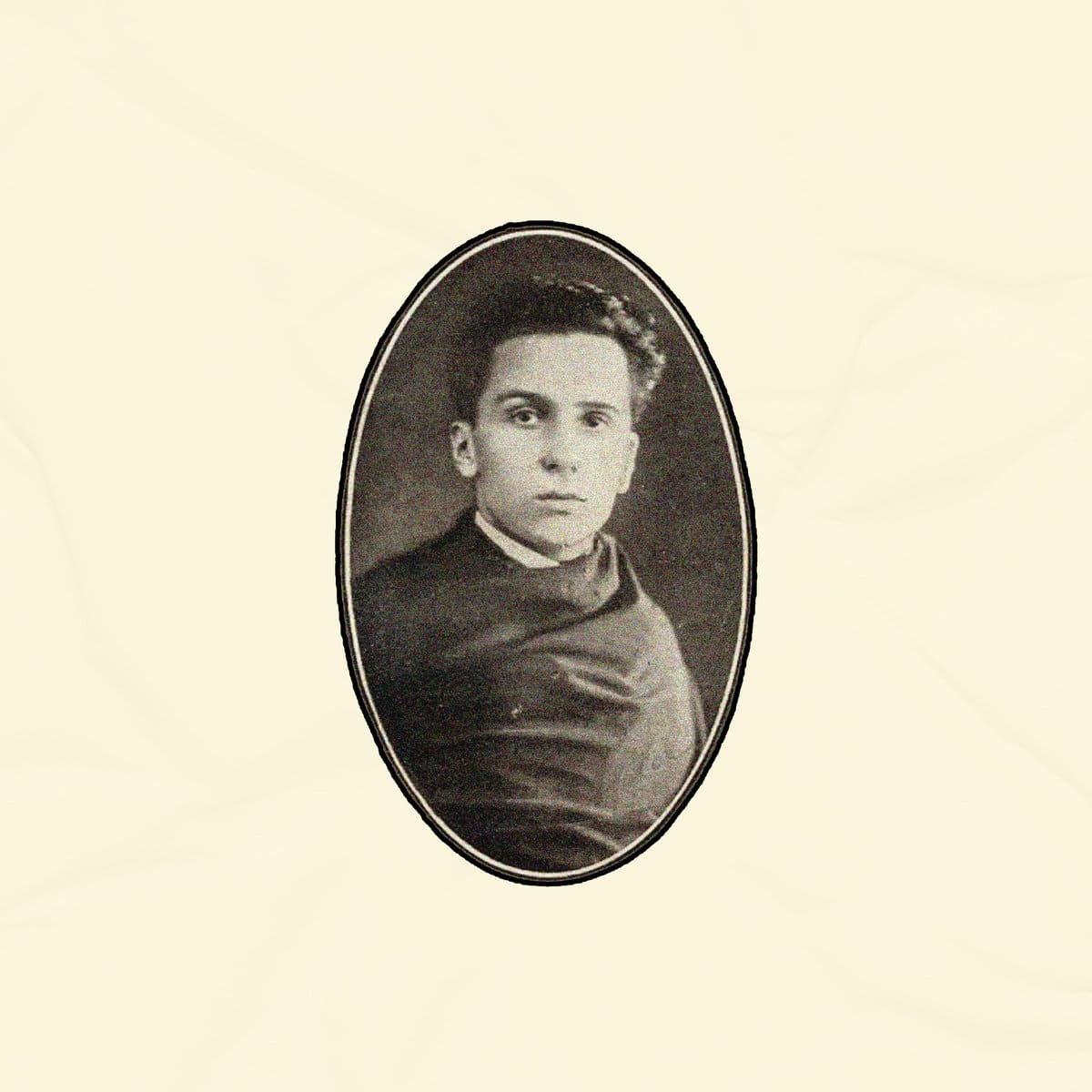
Ruby’s presence at the start is fitting, since Suite for Max Brown is a kind of family affair: “That’s my mother’s maiden name. Maxine Brown. Everybody calls her Max. I decided to call it Suite for Max Brown. The New Breed became a kind of tribute to my father because he passed away while I was making the album. The New Breed was a clothing store he owned when I was a kid, a store in Bridgeport, Connecticut, where I was born. I thought it would be nice this time to dedicate something to my mom while she’s still here to see it. I wish that my father could have been around to hear the tribute that I made for him. The picture on the cover of Max Brown is of my mom when she was nineteen.”
There is a multi-generational vibe to the music too, as Parker balances his contemporary digital explorations with excursions into older jazz. Along with original compositions, Parker includes “Gnarciss,” an interpretation of Joe Henderson’s “Black Narcissus” and John Coltrane’s “After the Rain” (from his 1963 Impressions album). Parker recalls, “I was drawn to jazz music as a kid. That was the first music that really resonated with me once I got heavily into music. When I was nine or ten years old, I immediately gravitated to jazz because there were so many unexpected things. Jazz led me into improvising, which led me into experimenting in a general way, into an experimental process of making music.”
Coltrane is a touchstone in Parker’s musical evolution. In fact, Parker recalls, he inadvertently found himself on a new musical path one night about fifteen years ago when he was deejaying at a Chicago bar and playing ‘Trane: “I used to deejay a lot when I lived in Chicago. This was before Serrato and people deejaying with computers. I had two records on two turntables and a mixer. I was spinning records one night and for about ten minutes I was able to perfectly synch up a Nobukazu Takemura record with the first movement of John Coltrane’s A Love Supreme and it had this free jazz, abstract jazz thing going on with a sequenced beat underneath. It sounded so good. That’s what I’m trying to do with Max Brown. It’s got a sequenced beat and there are musicians improvising on top or beneath the sequenced drum pattern. That’s what I was going for. Man vs machine.
“It’s a lot of experimenting, a lot of trial and error,” he admits. “I like to pursue situations that take me outside myself, where the things I come up with are things I didn’t really know I could do. I always look at this process as patchwork quilting. You take this stuff and stitch it together until a tapestry forms.”
—Michael Hill
Soon Over Babaluma

an observation platform.
 relative
relative